Significant limitations in intellectual functioning: To meet this criterion, a person's IQ score on an individual intelligence test (such as the Stanford-Binet or one of the Wechsler tests) must be two or more standard deviations below average.
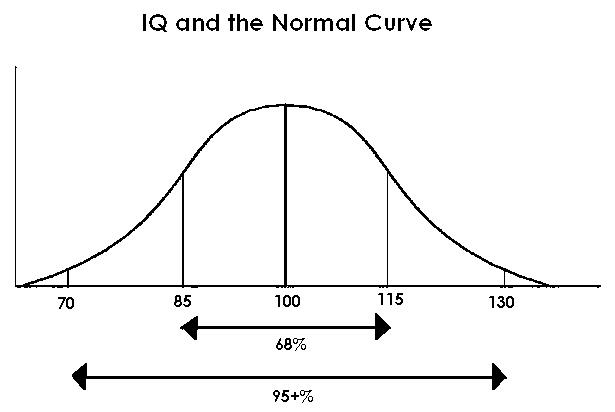
Since the standard deviation of an intelligence test is typically 15 (and the mean or average is IQ score is 100), a score two standard deviations below the mean is 70 (2 X 15 = 30, 100 - 30 = 70).
A standard deviation is a statistic that shows how scores are dispersed or spread from the mean or average. In a normal distribution (like that yielded by an intelligence test), about 68% of the scores are within one standard deviation of the mean and more than 95% of the scores are within two standards deviations of the mean. Therefore, fewer than 2 1/2% of IQ scores will be 70 or below (see diagram below).

It is important to note that the AAIDD definition refers to "sub-average intellectual functioning." Use of this phrase acknowledges the fact that a person's intellectual status may change. Therefore, an individual may meet this criterion at one point in his/her life, but not at another.
Limitations in adaptive behavior : Adaptive behavior is defined as " the collection of conceptual, social, and practical skills people have learned so they can function in their lives. Significant limitations . . . impact a person’s daily life and affect the ability to respond to . . . the environment.” (AAIDD, 2002). In order to meet this criterion, the person must perform at a level two or more standard deviations below the mean (average) in one of three areas (conceptual, social, or practical) or have an overall score that is two or more standard deviations below average on a standardized measure of adaptive behavior.
Developmental period: The
condition must have begun prior to age 18. The purpose of this criterion is to
emphasize that intellectual disabilities are developmental disabilities. Therefore, a person who suffers a stroke or a
serious head injury during adulthood would probably be considered to have a
traumatic brain injury and not an intellectual disability/mental retardation.